zscore()
The function zscore() will standardize a variable by converting all of its values to z-scores (i.e., the number of standard deviations the score is above or below the mean).
 Example 1:
Example 1:

Example 1:
Using the zscore() function alone will produce a list of z-scores for each value in the column of a specified variable.
# Get the z-scores for each thumb length
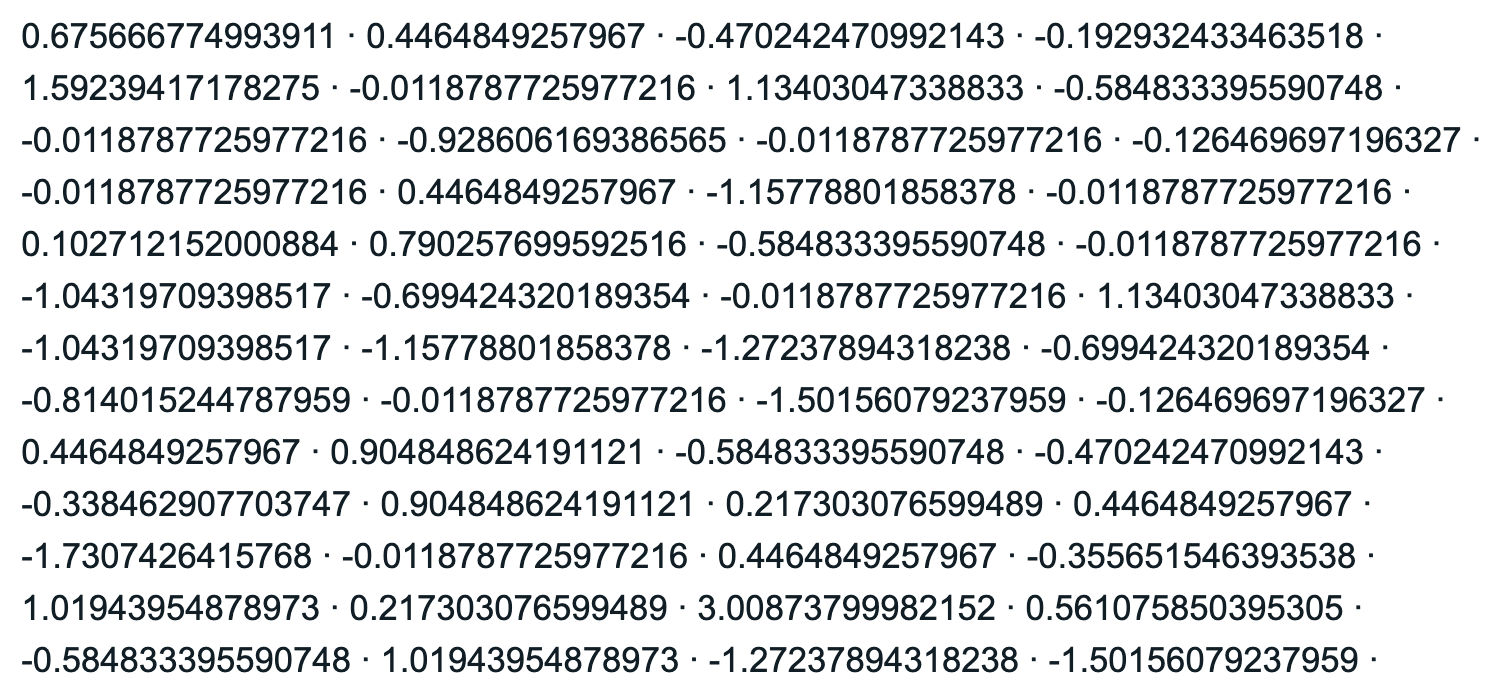
zscore(Fingers$Thumb)
Example output from running the code above (truncated):
 Example 2:
Example 2:

Example 2:
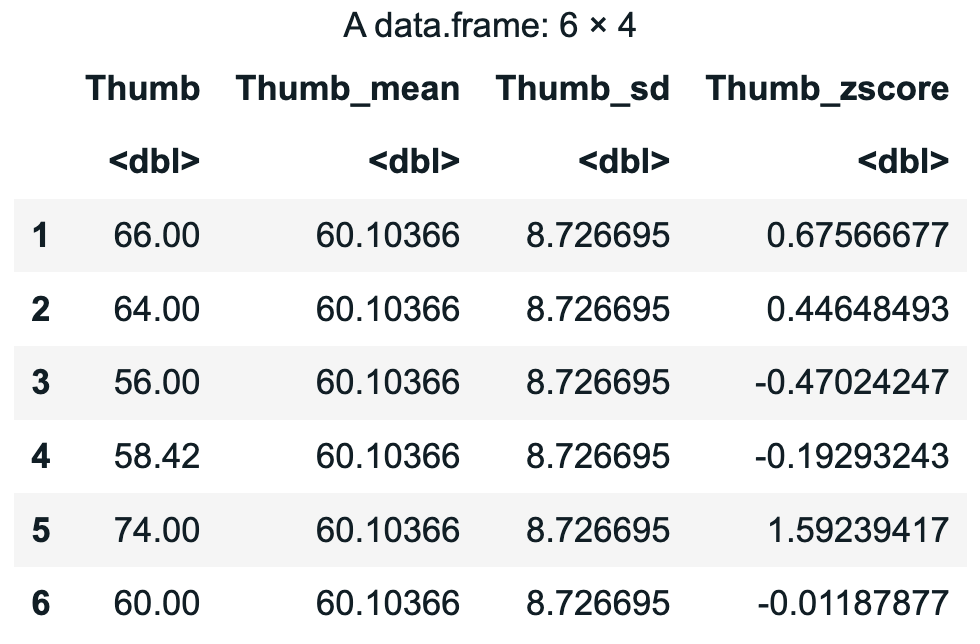
To see the z-scores in the context of the data frame, the code below will show a few rows of the data frame to compare: the actual thumb length values, the mean of Thumb, the standard deviation of Thumb, and the z-score (how many standard deviations the value is above or below the mean).
# Save the mean of Thumb into the data frame
Fingers$Thumb_mean <- mean(Fingers$Thumb)
# Save the standard deviation of Thumb into the data frame
Fingers$Thumb_sd <- sd(Fingers$Thumb)
# Save the z-scores of Thumb into the data frame
Fingers$Thumb_zscore <- zscore(Fingers$Thumb)
# Select the relevant variables and the first 6 rows of the data
head(select(Fingers, Thumb, Thumb_mean, Thumb_sd, Thumb_zscore))
Example output from running the code above: