predict()
The predict() function will generate the prediction(s) from a model.
 Example 1:
Example 1:
# Calculate the predictions from the Gender model of Thumb
# Use the lm() function to specify the model
predict(lm(Thumb ~ Gender, data = Fingers))
# Alt: Save the model into an object first
# then specify the name of the object as the argument
# (this method will produce the same output as the method above)
gender_model <- lm(Thumb ~ Gender, data = Fingers)
predict(gender_model)
Example output (truncated):
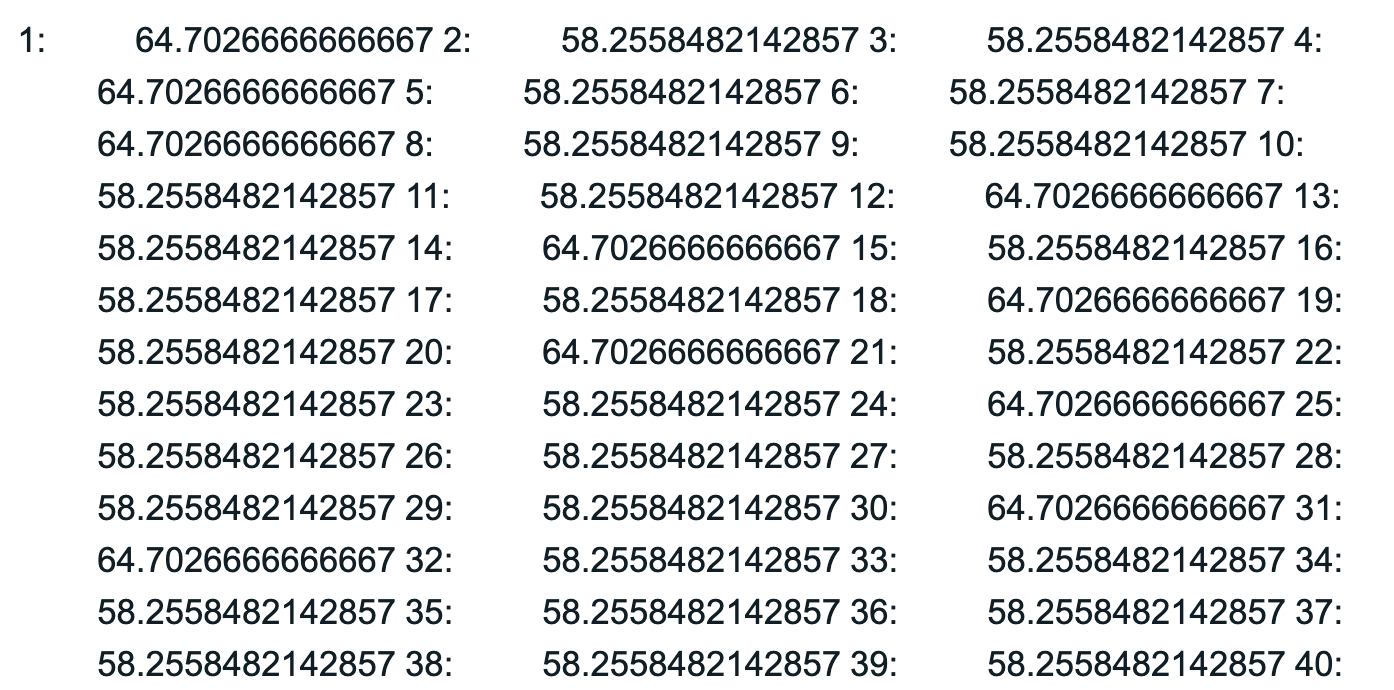
 Example 2:
Example 2:
To see each prediction in context, you might consider saving the predictions into the data frame as a new column to see more closely what the predict() function is doing.
# Save the predictions back into the data frame
gender_model <- lm(Thumb ~ Gender, data = Fingers)
Fingers$Thumb_predict <- predict(gender_model)
# Select a few rows and the relevant columns to compare
head(select(Fingers, Thumb, Gender, Thumb_predict))
Example output:
Related Articles
Statistical Model
A statistical model is a simplified way of describing how data are generated. It helps us separate what we can explain using known information from what we cannot explain perfectly. We use statistical models for three main purposes: (1) to understand ...resid()
The resid() function will calculate the residuals (error) from a model. That is, when given a model, it will take each case and calculate how far away the observed value is from the prediction of the model. Example 1: # Calculate the residuals from ...Variables
A variable is a measurable characteristic or attribute that can take on different values across cases (i.e., observational units such as people, companies, or time points). Types of Variables Variables can be classified by the type of values they ...Data Generating Process (DGP)
Data Generating Process (DGP) The Data Generating Process (DGP) refers to the underlying mechanism—real or hypothetical—that produces the data we observe. A DGP specifies how variables are related, how randomness enters the system, and how observed ...Empty Model
Empty Model (Null Model) An empty model is a statistical model that describes a quantitative outcome variable using only a single overall value, typically the mean of the response. It is called empty because it contains no explanatory (predictor) ...