anova()
The anova() function will compute an analysis of variance (ANOVA) for a model, and present the statistics in an ANOVA table, that includes:
- sums of squares (Sum Sq)
- degrees of freedom (Df)
- mean squares (Mean Sq)
- F values
- p-values (Pr(>F))
 Example 1:
Example 1:
Use the anova() function to get the ANOVA table for an empty model. You can save the model into an object first and use its name as the argument (Example 2 and Example 3), or you can use the lm() function directly in the anova() function (Example 1).
# Generate the ANOVA table for the empty model of Thumb
# using the lm() function within the anova() function
anova(lm(Thumb ~ NULL, data = Fingers))
Example output:
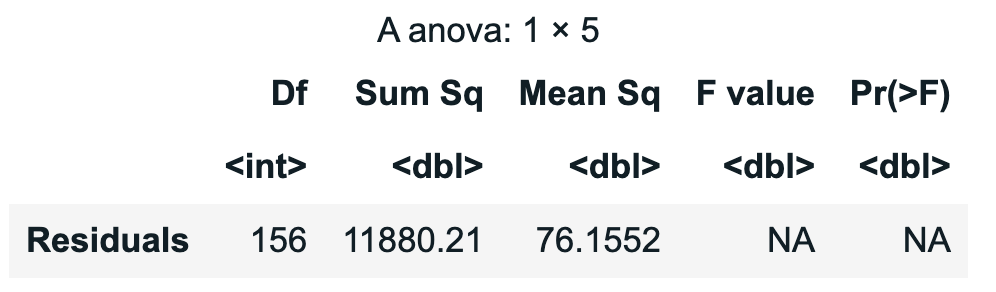
 Example 2:
Example 2:
Use the anova() function to get the ANOVA table for a model with a single predictor.
# Generate the ANOVA table for the Gender model of Thumb
# Save the model into an object first
gender_model <- lm(Thumb ~ Gender, data = Fingers)
anova(gender_model)
Example output:
 Example 3:
Example 3:
Use the anova() function to get the ANOVA table for a multivariate model.
# Generate the ANOVA table for the Gender + Height model of Thumb
gender_height_model <- lm(Thumb ~ Gender + Height, data = Fingers)
anova(gender_height_model)
Example output:
Related Articles
ANOVA
ANOVA means ANalaysis Of VAriance; partitions variation.supernova()
The supernova() function will compute an analysis of variance (ANOVA) for a model, and present the statistics in a modified ANOVA table, that includes: - sums of squares (SS) - degrees of freedom (df) - mean squares (MS) - proportional reduction in ...proportion reduction in error (PRE)
Proportion reduction in error (PRE) is the proportion of error that has been reduced by a more complex model compared with a simpler model, which in our course is always the empty model. When comparing to the empty model, PRE is calculated as SS ...